Molecular mechanism driving disulfide formation during FGF2 oligomerization and membrane translocation
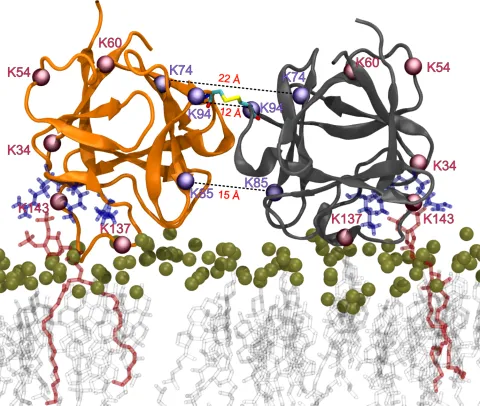
FGF2 is unconventionally secreted into the extracellular space by direct translocation across the plasma membrane. Interactions with the Na,K-ATPase and the phosphoinositide PI(4,5)P2 facilitate the recruitment of FGF2 to the inner face of the plasma membrane. However, pore formation and translocation depend on the covalent dimerization of FGF2 through disulfide bond formation. The goal of this project is to uncover the molecular machinery and mechanism by which disulfide-linked FGF2 dimers are formed at the plasma membrane.
Biochemistry and Cell Biology
Walter Nickel
Tobias Dick
