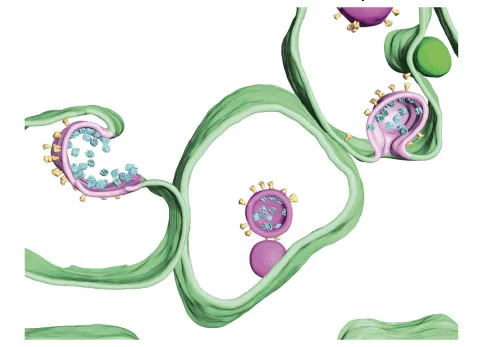
This project will focus on the membrane remodeling that is critical for the assembly and replication of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. We hypothesize that SARS-CoV-2 assembly involves membrane bending induced by both viral transmembrane proteins and adhesion of biomolecular condensates formed by viral ribonucleoprotein. We will use in situ cryo-electron tomography to study virus assembly and replication vesicles composed of different sets of viral proteins. This will be combined with mathematical continuum models to achieve a quantitative understanding of the interplay between membrane bending by proteins and by adhesion of biomolecular condensates. In the long term, this approach will provide a better understanding of the complex membrane remodeling processes occurring during viral infections.
